A BRIEF OVERVIEW OF THE PREVIOUS CLASS (05:15 PM)
TROPICAL DRY EVERGREEN (05:19 PM)
- Conditions
- Dry summer, wet Winter- In India it can be seen in the Coromandel coast
-

- Trees- Neem, Tamarind, Jamun, Toddy palm
TROPICAL DECIDUOUS (05:23 PM)
- Characteristics- Capacity to shed the leaves
- Tropical Moist Deciduous
- Precipitation- 100-200 cm
- Characteristics- Thick forest- Dense growth, Multilayered also these are very similar to evergreen forests in terms of diversity
- Region- Wetter parts of Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Karnataka, Chattisgarh, Jharkhand, Odisha
- Trees- Teak (Shagwan), Sal, Almond, Jamun, Seesham (Rosewood of North India), Sandalwood (Shade-loving plant, it takes 30-40 years to mature, Mostly found in Karnataka).
- [* Teak does not survive cold conditions and in Northern plains it is replaced by sal, In central India teaks are mostly found]
- Tropical Dry deciduous
- Precipitation- 70-100 cm
- Characteristics- Low density, low diversity
-
.png)
- A wide area covering north to south from the Himalayas to Kanyakumari except the regions of Moist deciduous and Tropical thorn
- Trees- Bamboo (* For the purpose of the Indian Forest Act, it is classified as a Tree, Bamboo which grows outside of a forest area can be cut.), Sandalwood, Red Sandalwood (Red Sanders) (* It is one of the most smuggled goods in the world. It has huge demand in China, South Korea, etc)
-
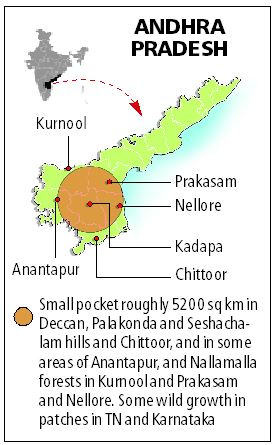

- Conditions for red sanders- Low precipitation (70-100), sloppy mountains.
- Red sanders are used in Furniture
TROPICAL THORN (05:44 PM)
- Precipitation- less than 70 cm.
- They adapt to lesser water availability
- Regions- Rajasthan, Gujarat, parts of Punjab- Haryana, Rain Shadow region of Deccan plateau.
- Trees- Khair tree, Acacia Katechu, Axlewood, Babool, Neem, Date, Sandalwood trees
- [* Prosopis Juliflora is an invasive species and not a tropical thorn forest]
MONTANE VEGETATION (05:49 PM)
- It is grown in High altitude areas
- Types of Montane Vegetation
- a) Ganga plain- Dry Deciduous
- b) Upto 1500 meters- Mixed forest.
- c) 1500-3500 meters- Coniferous forest
- d) Beyond 3500- Alpine vegetation. (Short bushes, Grass etc. A special type of Alpine vegetation/ grassland is found called BUGYALS in Uttarakhand)
-

- Bugyals are very nutritious for cattle. People move from the valley to Bugyals in summer along with their cattle and move towards the valley in winter. This is called Transhumance.
- This is practised by Gaddis, Bhotiyas, Bakarwals, and Gujjars tribes in India.
- Areas of Montane forest- Vindhyas, Satpuras, High elevated regions of Western Ghats
- Nilgiri- The grassland is throughout the year. [* Because of low temperature so stronger vegetation is not found therefore grassland is found. In valleys, trees are found]. Shola Forest is found in these areas. These are the Montane grassland.
- Trees of Montane vegetation- Deodar tree, Chir Pine tree (softwood, These are in higher demand in the Lumbering industry. In hot weather the needle-like leaves became too dry and they catch the fire very easily. ), Oaktree, Maplewood, Juniper tree, Rhododendron (Known for its very beautiful flowers, used in Tibetan Monastery).
LITTORAL AND SWAMP FOREST (06:04 PM)
- These are commonly referred to as Mangroves. These are the only vegetation that can grow in coastal regions.
- Characteristics-
-
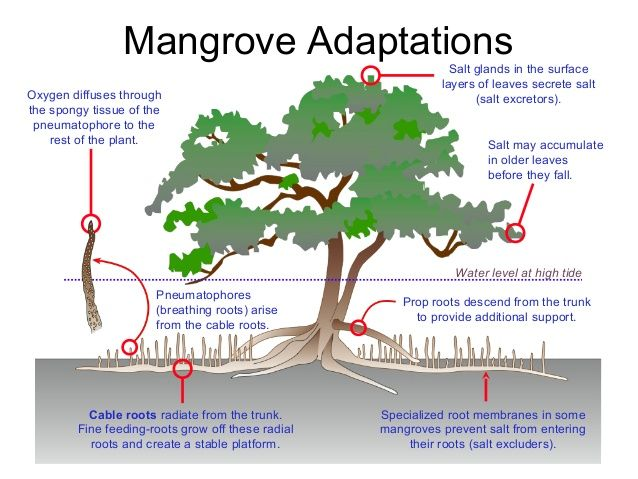
- Aerial roots- called as Pnematophores
- Stilt Root system- It accommodates the varying level of water also, It provides higher strength
- Impermeable roots
- Buoyant seeds- Seeds are floating. It has easy dispersal of seeds.
- Controlled opening of stomata
- Examples of trees- Sundari Tree, Brugeira, Sonneratia, Agar Agar
- Characteristics- These are evergreen species, Short growing, majorly found in Deltas.
- Regions- Sundarbans, Kaveri Delta, Coringa Delta, Picchavaram Mangroves, Bhitarkanika mangroves, Mutupet mangroves, Coondapur mangroves.
-

- Significance of Mangroves
- It is the only type of vegetation that survives in the coastal region
- It provides habitat to various species. [* Species found- Tigers of Sundarban are capable of swimming and hunting, Fishing cat, Saltwater crocodile]
- It prevents coastal erosion.
- It also reduces the impact of tsunamis and cyclones.
- Ecological role- Water Filtration, settling the sediments, nutrient recycling, initiator of the food chain (Mangrove leaves- when falls and decomposes becomes food for insects and starts the food chain).
- Economic value (Source of timber), Tourism.
- It helps in Carbon sequestration- Storage of carbon.
- Reasons for Mangrove Depletion in India
- Overharvesting
- Coastal Encroachment
- Change in River course- Natural or Artificial
- Pollution- Water Pollution, Thermal pollution
- Oil spill- destroys the ecosystem.
- Government scheme- MISHTI scheme
AGRICULTURE (06:23 PM)
- World Agriculture types
- 10 major types- 4 types in Tropical regions and 6 types in Temperate regions
-
Tropical Region
- Nomadic Herding
- Shifting cultivation
- Intensive subsistence
- Plantation Agriculture
Temperate Region
- Mediterranean
- Extensive commercial grain
- Commercial Ranching
- Mixed farming
- Dairy farming
- Truck Farming
Reasons
- Higher population
- Land fragmentation
- Low investment
- Dominated by manual labour
- Traditional methods of agriculture
Reasons
- Low population
- Large tracts of land
- High investment
- Dominated by Machines
- Scientific methods of agriculture
-
NOMADIC HERDING (06:31 PM)
- It is one of the most primitive modes of agriculture.
- It is the simplest form of Pastrolism (taking care of animals)
- They are dependent on animals rather than crops. They are dependent on Milk, meat, hair, silk
- Animals- Camel in North Africa, and West Asia; Horses in Central Asia; Yak & Lama in Mongolia, China, and Tibet; Ships & Goats in semi Arid and dry regions (They practice transhumance)
SHIFTING CULTIVATION (06:35 PM)
- They are practised by Tribes living in the forest.
- Forest is owned by the community. Forest is divided into multiple patches. At first individual patch is selected and it is burnt down (They think that the burning of trees adds nutrients to the soil), Wild grain is cultivated then, and Soon soil will lose fertility.
- This will be followed by shifting to a second patch.
- Regions- North East (Jhuming cultivation), Some patches of western Ghats and Srilanka, South East Asia, Congo basin, Amazon Basin, Parts of Venezuela and Mexico.
INTENSIVE SUBSISTENCE AGRICULTURE (06:41 PM)
- A most common type of agriculture practised in Developing and Less developed countries
- Characteristics
- Small and highly fragmented land holdings
- The high density of population
- Dominant manual labour.
- Multiple crops per year.
- Very high agricultural productivity but low per capita production.
- Regions- Entire South Asia including the Deltas of Ganga, Brahmaputra, and Indus; Parts of eastern China.
PLANTATION AGRICULTURE (06:45 PM)
- It is characterized by large estates established by colonial rulers.
- It is highly capital-intensive and highly centralized. They brought Scientific varieties of plants and seeds.
- The intention was export-oriented
- It was dependent on manual labour.
- Regions-
- In India- Coffee, Tea, and Rubber plantation
- In Malaysia- Rubber plantation
- In Indonesia- Sugarcane plantation
- In the Pacific- Fiji- Sugarcane plantation
- In South Africa- Sugarcane plantation
- In West Africa- Cocoa and coffee plantation
- In West Indies- Banana and Sugarcane plantation
MEDITERRANEAN TYPE OF AGRICULTURE (07:17 PM)
- These are short bushes, Drought resistant, Deep root system
- Examples- Grapes, Oranges, Olives, and other citrus fruits
-

EXTENSIVE COMMERCIAL GRAIN FARMING (07:20 PM)
- It is a steppe type of climate.
- It is found in temperate grasslands- Pampas, velds, downs, Prairies, Steppes, etc.
- Precipitation- Moderate precipitation but throughout the year i.e. both in summer and winter.
- Soil- Black earth (Chernozem) (* High amount of calcium carbonate )
- Characteristics- Extensive means a very large area of the farm, very low population density, dominated by wheat monoculture, High mechanization, and a Scientifically managed variety of crops, High Per capita output but low per hectare output.
-
- It is not found in central Asian country's grasslands. They do Horse rearing.
COMMERCIAL LIVESTOCK RANCHING (07:29 PM)
- It is the opposite of Nomadic herding.
- A large area is available.
- Commercial raising livestock over extensive areas.
- Animals- Sheep, Goats, Cattle, Horses.
- Scientific methods of breeding of animals.
- Ranches are very large with continuous vegetative cover. They maintain the large no. of sheep with the highly trained dogs
-

- Characteristics- Only meat
MIXED FARMING (07:36 PM)
- Both Agriculture and Animal rearing/ livestock.
- Crops are useful for both human as well as livestock consumption. Example- Maize.
- It involves high expenditure on machines and farm buildings.
- It gives high returns
- Regions- East of prairies, Western Europe (Germany, France), Northeast Argentina, Southeast Australia.
COMMERCIAL DAIRY FARMING (07:40 PM)
- Milk and milk products
- It requires high capital. It is highly labour-intensive.
- Productivity is very high
- Regions- Northeast USA, Northwest Europe (Netherland, Denmark, Sweden), Southeast Australia and Newzealand, Eastern Argentina
TRUCK FARMING (07:44 PM)
- Growing perishable fruits and vegetables at a distance that can be covered in one night.
- It is also called Market gardening. It is also called factory Farming.
- Regions- Northeast USA, Northwest Europe, etc.
INDIAN AGRICULTURE (07:47 PM)
LAND USE CATEGORIES IN INDIA
- 1) Forest- Cannot be used for settlement, Agriculture, etc
- 2) Area under non-agricultural use- It includes all the settlements, places of working, place of settlement, infrastructures such as buildings & road
- 3) Barren and wasteland- It can not be used for agriculture with presently available technology. example- deserts, Chambal ravens
- 4) Permanent pasture and tree crops.
- 5) Net sown area- The area which is under cultivation in the current year is the net sown area. The total area under cultivation where the area which is sown multiple times is accounted for multiple times is called gross crop area.
- Cropping intensity, CI= GCA/ NSA * 100
- 6) Current fallow- The land which is left uncultivated in the last year is called as current fallow.
- 7) Fallow other than current fallow- Which is left uncultivated for more than one year but less than 5 years.
- 8) Culturable wasteland- The land which is left uncultivated for more than 5 years.
-
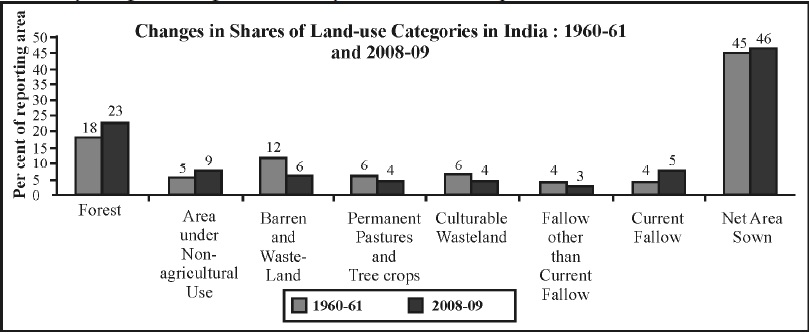
- Trends
- 1) Net sown area- There is a slight increase since independence due to the expansion of agriculture
- 2) Forest Area- There is a slight increase due to efforts of the forest department
- 3) Non-agricultural use- There is an increase due to urbanization.
- 4) Barren and wasteland
- The current fallow has also increased.
- Fallow other than the current fallow and culturable wasteland has decreased
The topic for the next class- Indian cropping conditions, cropping patterns, Green Revolution, etc.